Managing Structured Data with EncompaaS

Structured data in relational databases revolutionized the management of transactional data. Today, large organizations have 100’s and sometimes 1,000’s of databases and associated applications, inevitably modified over time as business requirements evolved. To make sense of structured data, every organization also uses tools to create easily understandable business objects - a software representation that has a set of attributes and values, operations, and relationships to other business objects, and models business behaviour.
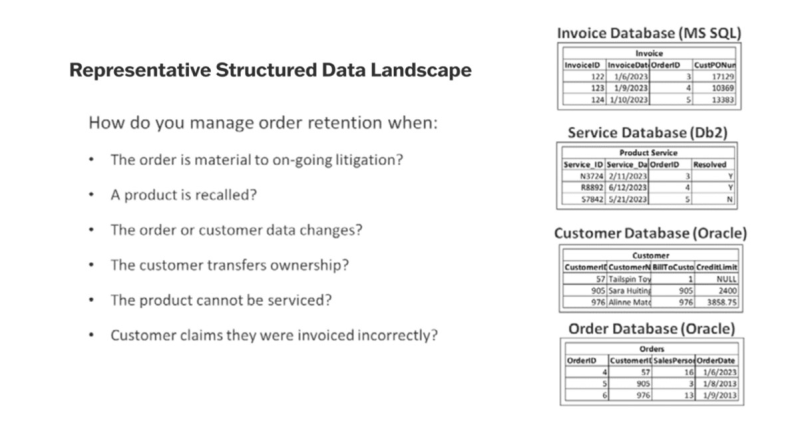
Even the simplest Sales database, for example, will have 20+ tables coming from more than one database schema or even completely different databases, making the data unintelligible to a business user.
Business objects allow organizations to process, report and present information that answers questions such as:
- Which sales in the last fiscal are now identified as subject to legal hold?
- For two products that were recalled by the distributor, what is our liability and inventory?
- Who are my bottom three sales representatives on performance plans in the current fiscal year?
- How do we discover everything relevant to a legal action regarding service calls?
Equally important, these same business objects are subject to information lifecycle management. How do you apply retention to structured data business objects? How do you successfully manage a Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) for meeting privacy guidelines? How does the organization ensure effective and comprehensive eDiscovery? How do you apply a Legal Hold or other label to guide lifecycle management?
Information lifecycle management is difficult and complex for structured data (compared to unstructured data) because it exists as disparate, related database records, often across multiple systems. Moreover, very few database applications support concepts like retention, legal hold, records classification or disposition.
Initially organizations often react by implementing complex, manual, and overly broad information management practices, which are often at odds with best practices. Even though only a handful of records are relevant, for example, the easiest approach for many organizations is to save entire databases and tables.
Similarly, a DSAR might make copies of the sensitive privacy or health data being managed, while a legal hold misses important data because nobody knew it existed.
Traditional approaches to this problem focus on information management via applications. Given multiple applications and/or constantly evolved governance rules, organizations end up continuously updating and testing applications.
Another traditional approach pioneered with unstructured data is to use software applications or agents to provide governance through the capabilities of the source repository. This approach might work for an Enterprise Content Management (ECM) system or (with some limitations) a file system but is virtually useless with rows in structured databases.
EncompaaS is a state-of-the-art information management application specifically designed to manage both structured and unstructured data in the same way. EncompaaS allows organizations to manage structured data in place (manage-in-place, or MIP) and use the same capabilities and tools commonly exploited for unstructured data:
- Search
- Classify (using artificial intelligence/machine learning)
- Label/Tag (using artificial intelligence/machine learning)
- Assign a retention schedule
- Apply legal hold
- Defensibly dispose at the end of its information lifecycle
With EncompaaS, customers can define and create their own business objects based on their unique data and requirements; for example, using the information above, easily understandable Sales business objects are created representing a single order from that customer.
The EncompaaS approach has significant technical and business advantages over traditional approaches:
- Comprehensive auditing of business objects throughout their information lifecycle.
- No application or user interface changes.
- Protects against inadvertent or malicious data deletion by users or applications.
- Defensibly dispose of structured data at the end of its lifecycle—using the same capabilities used for defensible disposition of unstructured data.
- Defensibly dispose of structured data consistent with enterprise policies, procedures and best practices for deletion from databases.
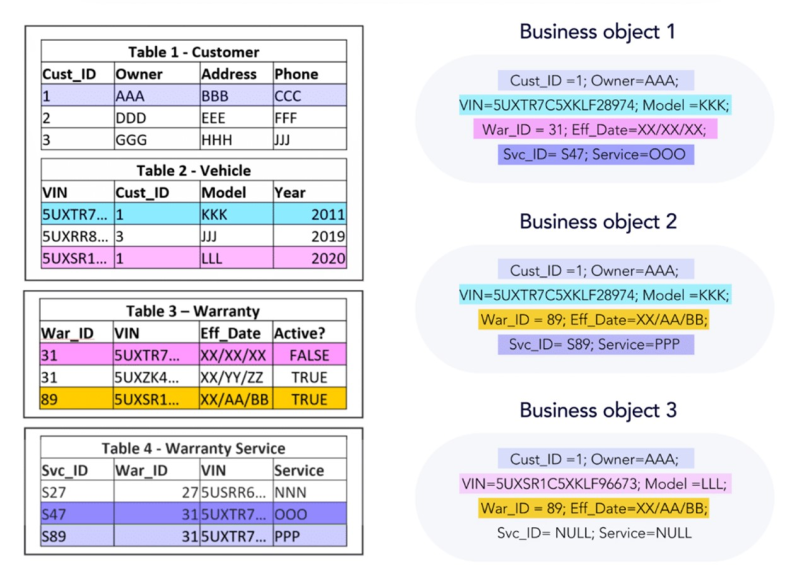
Information lifecycle management continues to evolve from electronic files in disparate systems to business objects representing structured data from multiple data sources.
EncompaaS provides a state-of-the-art, native-cloud solution that allows organizations to consistently apply their knowledge and existing practices identically to both structured and unstructured data. The result is lower costs, enhanced compliance, reduced risk and greater data quality.
Most important, the EncompaaS solution provides both complete data control for lifecycle management as well as new value to support business decision making.
David Gould is Chief Customer Officer at EncompaaS. Contacvt him at david.gould@encompaas.cloud for more information.
